I kinda get it but someone ( @Help!I'maRock! particularly) explain it to me. I seem to like it. What is "hard clip"?
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
So talking to me about "soft clip"
- Thread starter Mark Wein
- Start date
Help!I'maRock!
Mediocringly Derivative
These are the best visual representations I can give you:
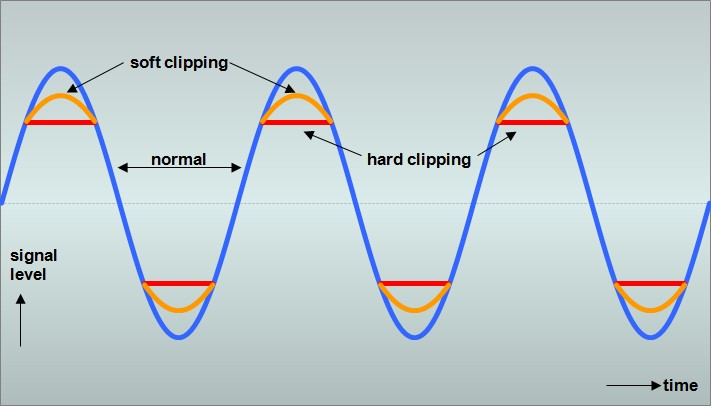
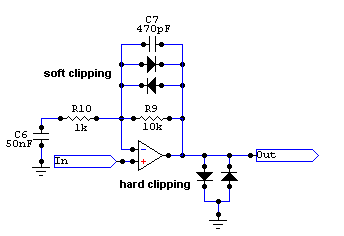


Help!I'maRock!
Mediocringly Derivative
So what pedals are "hard clip"?
A good example is anything that uses FETs for the actual distortion. That could range from something like the Way Huge Red Llama, which uses a CMOS chip; to the Catalinbread Dirty Little Secret (and their other preamp pedals) that use JFETs. I'm sure @RyanNo3, @Modern Saint, and @Wyatt could give many more examples and better explanations.
jp_nyc
Kick Henry Jackassowski
So what pedals are "hard clip"?
Most non-tube distortion circuits are hard clip. It’s most intense in fuzz and muff style circuits, where the waveform is almost converted to a square wave.
Exactly.The capacitor looks like a open electrically, until the voltage on the capacitor builds up to forward bias the diodes. Then the soft clip occurs. The time needed depends on the capacitor; larger cap = more time.
I was going to chime in with that just now.
But, while I understand what the clipping circuits are doing in that schematic, I'm not sure I know what a soft clipping circuit sounds like.
Help!I'maRock!
Mediocringly Derivative
Exactly.
I was going to chime in with that just now.
But, while I understand what the clipping circuits are doing in that schematic, I'm not sure I know what a soft clipping circuit sounds like.
Ever played a Tubescreamer or a horsie pedal?
Sure, aren't the unicorn tears are in the diodes!Ever played a Tubescreamer or a horsie pedal?
RyanNo3
Pedals - Pedals - Pedals
Most non-tube distortion circuits are hard clip. It’s most intense in fuzz and muff style circuits, where the waveform is almost converted to a square wave.
+1 to this
Yes - So *I feel* it's marketing jargon. You'll see a lot of pedals that use Germanium diodes market as overdrive pedals (TS9, Klon in any variation) or Silicon diodes with a resistor to taper the waveform. You could just make an overdrive pedal with an op amp and adjusting the gain resistors based on the input of the opamp. The waveform get's bigger and a little choppy.
Market as distortion and it's full fledged combination of signal passing through or across the silicon resistors. That do the hard chopped square waves. To me, anything that hard clips, has a buzz saw sound to it. Think ZVex Fuzzolo, Fulltone 69, DS-1.
** Disclaimer: Just from personal experience and 'some' technical background **
RyanNo3
Pedals - Pedals - Pedals
The capacitor looks like a open electrically, until the voltage on the capacitor builds up to forward bias the diodes. Then the soft clip occurs. The time needed depends on the capacitor; larger cap = more time.
And bigger cap, more low frequencies get through which I would expect creates "warmth"
Modern Saint
Starve your Fear, Feed your Dream!
If the word "Distortion" is in the pedals name, it will be hard clip. @Help!I'maRock! post is perfect in comparison of the different clip modes.
When you hard clip a sine wave, you are cutting off the top of the sine wave and force creating a square wave.
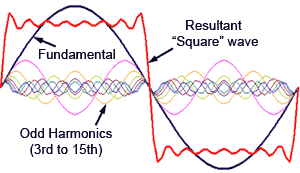
Square waves are rich in odd harmonics hence the result in a harsh or buzzier-distorted sound. Increase the distortion knob and you increase the amplitude of the sine wave and the result is hard clipping. Basically all OD and Distortion boxes operate on this concept pending primarily to 1) gain and 2) the placement of the diodes which provide either soft clipping or hard clipping.
Examples of hard clipping pedals are: MXR Distortion +, BOSS DS-1, Metal Zone, Marshall Guv'nor
If you read schematics, you will usually find Diodes in parallel on the output of gain stages. The Marshall Guv'nor uses LED Diodes to clip instead instead of Silicon Diodes. LED's have a higher threshold providing later breakup but the concept is the same, you are hard clipping the output signal equally.

Examples of soft clipping pedals are: Tube Screamer, Xotic AC. Notice the diodes are in parallel to the IC chip. This usually happens in the first stage of the IC.

FET's are similar to Tubes in the way they operate. The overdriven sound is a softer clip but you are clipping the FET which is a different principle as compared to above.
Examples of FET type overdrives are: Wampler Pinnacle, Fulltone OCD, etc.
Please note that these are some of the basic rules. Companies will combine the above to create their own unique OD.
When you hard clip a sine wave, you are cutting off the top of the sine wave and force creating a square wave.

Square waves are rich in odd harmonics hence the result in a harsh or buzzier-distorted sound. Increase the distortion knob and you increase the amplitude of the sine wave and the result is hard clipping. Basically all OD and Distortion boxes operate on this concept pending primarily to 1) gain and 2) the placement of the diodes which provide either soft clipping or hard clipping.
Examples of hard clipping pedals are: MXR Distortion +, BOSS DS-1, Metal Zone, Marshall Guv'nor
If you read schematics, you will usually find Diodes in parallel on the output of gain stages. The Marshall Guv'nor uses LED Diodes to clip instead instead of Silicon Diodes. LED's have a higher threshold providing later breakup but the concept is the same, you are hard clipping the output signal equally.
Examples of soft clipping pedals are: Tube Screamer, Xotic AC. Notice the diodes are in parallel to the IC chip. This usually happens in the first stage of the IC.
FET's are similar to Tubes in the way they operate. The overdriven sound is a softer clip but you are clipping the FET which is a different principle as compared to above.
Examples of FET type overdrives are: Wampler Pinnacle, Fulltone OCD, etc.
Please note that these are some of the basic rules. Companies will combine the above to create their own unique OD.
Modern Saint
Starve your Fear, Feed your Dream!
The capacitor looks like a open electrically, until the voltage on the capacitor builds up to forward bias the diodes. Then the soft clip occurs. The time needed depends on the capacitor; larger cap = more time.
Actually caps in conjunction with resistors affect the what frequencies are: 1) passed; 2) blocked.
In the basic form, the circuit below is a low pass filter. In regards to freq, low frequencies are passed and high are shunted to ground, hence blocked.
And here is a high pass filter, where high frequencies will pas through the circuit and low frequencies are reduced.
Please note that the 2 circuits above are dependent on what the component values are.
